What is Laravel Request Lifecycle?
The Laravel Request Lifecycle describes how an HTTP request is handled by the Laravel framework from the moment it enters the application until a response is returned to the client.
Step 1. Incoming HTTP Request
A request is initiated by the client (browser, mobile app, API tool) and sent to the Laravel application.
The request contains -
• HTTP method
• URI
• Headers
• Body data
A user sends a request via browser or API - GET /products
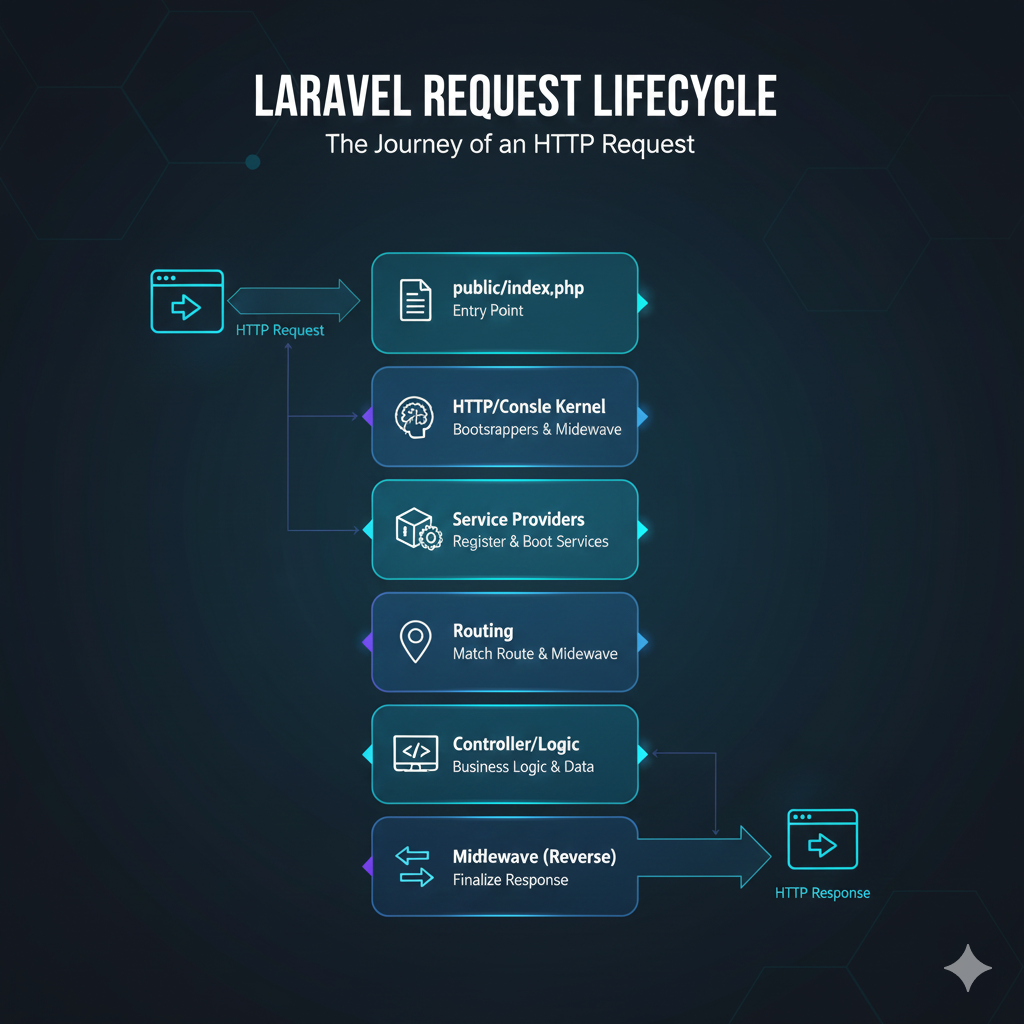
Step 2. Entry Point (public/index.php)
public/index.php is the entry point of a Laravel application.
All incoming requests are handled from this file, and the framework is bootstrapped here.
This file -
• Loads Composer autoloader
• Bootstraps the Laravel application
• Passes the request to the HTTP kernel
Step 3. HTTP Kernel (App\Http\Kernel.php)
The HTTP Kernel is responsible for -
• Bootstrapping the application
• Loading global and route middleware
• Dispatching the request to the router
It defines -
• Global middleware
• Middleware groups (web, api)
• Route middleware
Step 4. Middleware Execution
Middleware acts as a filtering layer.
Common responsibilities -
• Authentication
• Authorization
• CSRF protection
• Request sanitization
If a middleware fails, the request is terminated. If successful, the request proceeds.
Step 5. Service Providers (Bootstrapping)
Service Providers Laravel ke core components ko load karte hain jaise -
• Database
• Routes
• Sessions
• Authentication
Step 6. Routing
Laravel matches the incoming request with a route defined in -
• routes/web.php
• routes/api.php
If a match is found, the corresponding controller or closure is executed. If not, Laravel returns a 404 response.
Step 7. Controller
Controllers handle application logic.
They -
• Fetching data from database
• Validations
• Returning views or JSON responses
Step 8. Model & Database
Laravel uses Eloquent ORM to interact with the database.
Models represent database tables and allow CRUD operations without writing raw SQL.
Step 9. Response View
The controller returns a response, which can be -
• A Blade view
• JSON response
• Redirect response
Blade compiles templates into plain PHP and renders HTML.
Step 10. Response back through Middleware
The response passes back through the middleware stack in reverse order before reaching the browser.
Step 11. Browser Receives Response
The browser receives the final response and renders it for the user.
In Short Explanation of Laravel Request Lifecycle -
Laravel Request Lifecycle explains how an HTTP request is handled by Laravel.
When a user sends a request, it first enters through public/index.php, then goes to the HTTP Kernel, where service providers are loaded and middleware is executed.
After that, Laravel matches the request with a route, sends it to the controller, processes the logic (using models if needed), and finally returns a response (view/JSON) back to the browser.
Laravel Request Lifecycle is the flow of a request from index.php → middleware → routes → controller → response.
In hindi -
Laravel Request Lifecycle batata hai ki user ki request Laravel me kaise process hoti hai. Request sabse pehle public/index.php me aati hai, phir HTTP Kernel middleware aur services load karta hai. Uske baad request route se match hoti hai, controller me logic execute hota hai, aur end me response user ko return kar diya jata hai.

Blog Comments (0)